Hamish Burke | 2025-04-23
Related to: #databases #programming
SQL
- Once Relational Data Model schema made
- Can use as
- Declarative and set oriented
- Order doesn't matter
- Names are not case-sensitive
- Uses BNF Notation to describe SQL syntax
Views (virtual tables)
- Restricted access to a database
- Stored in the catalog (metadata) of the DBMS
- Acts as a table, though queries the info every time its accessed
CREATE VIEW 301Students AS
SELECT s.LName as Surname, g.Grade
FROM Students s, Grades g
WHERE s.StudId = g.StudId
AND g.code = '301';
-- Query created view
SELECT * FROM 301Students;
-- Show all views
SHOW FULL TABLES WHERE table_type LIKE "%VIEW";
-- Drop a view
DROP VIEW view_name;
Creating the DB
Domains
CREATE DOMAIN <domain_name>
[AS] <data_type>
[DEFAULT <value>]
[{CONSTRAINT <name> <constraint>,...}]
CREATE DOMAIN AGE
AS INT
DAFAULT 1
CONSTRAINT idnoconstr
CHECK (VALUE > 0 AND VALUE <= 100);
Tables
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (
{<attribute_declaration> , ...}
[,{[CONSTRAINT <name>] <table_constraint>, ...}]
);
CREATE TABLE COURSE(
CourId CHAR(7) CONSTRAINT cspk PRIMARY KEY,
CName CHAR(15) NOT NULL,
Points INT NOT NULL CONSTRAINT pointschk
CHECK (Points >= 0 AND Points <= 50),
Dept CHAR(25)
);
SELECT *
FROM GRADES
WHERE Grade NOT IN (
SELECT Grade
FROM GRADES
WHERE Grade NOT NULL
);
Attribute Constraints
NOT NULL
(PRIMARY KEY | UNIQUE)
REFERENCES <refed_table_name>
[<refed_table_attribute>]
[ON DELETE (NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT)]
[ON UPDATE (NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT)]
[MATCH FULL | MATCH PARTIAL]
CHECK( <conditional_expression>)
Table Constraints
PRIMARY KEY( <attribute_list> )
| UNIQUE(<attribute_list>)
| FOREIGN KEY <attribute_list>
REFERENCES <referenced_table_name>
[<referenced_attribute_list>]
[ON DELETE (NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT)]
[ON UPDATE (NO ACTION | CASCADE | SET NULL | SET DEFAULT)]
[MATCH FULL | MATCH PARTIAL]
Modifying the DB
INSERT
- Assumes values appear in the same order as the
CREATE TABLEcommand
INSERT INTO <table_name> [<attribute_list>]
(VALUES (<value_list>) | SELECT ...)
- Though can specify order of attributes
- Missing attributes get set to null, or
DEFAULTvalue (if set)
INSERT INTO STUDENT(FName,LName,StuId)
VALUES('Ann','Bole',11111);
Can make a temp table, to aggregate info
- Eg count of course
CREATE TABLE StudentInfo(
StudId INT PRIMARY KEY,
LName CHAR(15) NOT NULL,
NoOfCourses INT
);
INSERT INTO StudentInfo
SELECT s.StuId, LName, COUNT(*) AS NoOfCourses
From Student s, Grades g
WHERE s.StudId = g.StudId
GROUP BY StudId, LName;
UPDATE
UPDATE <table_name>
SET <attribute_name> = <value_expression>
{, <attribute_name = <value_expression> }
[WHERE <condition>]
- All people taking
C302getA+ - If no
WHERE, all rows will change toA+
UPDATE GRADES
SET Grade = 'A+'
WHERE CourId = 'C302';
DELETE
DELETE FROM <table_name> [WHERE <condition>]
- Delete all the delete who did
C302 - Without
WHEREwill delete all records- Different to
DROP, as keeps table structure
- Different to
DELETE FORM STUDENT
WHERE StudId IN
(SELECT s.StuId
FROM STUDENT s, GRADES g
WHERE s.StudId = g.StuId AND CourId = 'C302');
Queries
Test queries
- Get first/last name of comp students
SELECT FName, LName
FROM STUDENT
WHERE Major = 'COMP';
- Find all different grade
SELECT DISTINCT Grade
FROM GRADES;
- Retrieve course names of all 300 level courses
_replaces one character%replaces an arbitrary number of chars
SELECT CName FROM COURSE
WHERE CName LIKE '____3%';
- Show grades tables, sorted
SELECT *
FROM GRADES
ORDER BY StudId ASC, CourId DESC;
- Retrieve course names with grades and the surname for Student James
SELECT c.CName, Grade, LName as Surname,
FROM STUDENT s, GRADES g, COURSE c
WHERE FName = 'James' AND s.StudId = g.StudId
AND c.CourId = g.CourId;
| CName | Grade | Surname |
|---|---|---|
| DB Sys | A+ | Bond |
| SofEng | A | Bond |
| DisMat | A+ | Bond |
Nested Query
-
Comparing a tuple to a collection of tuples
-
Retrieve first names of students that passed M214
SELECT FName
FROM STUDENT s
WHERE s.StudId IN -- inner query getting everyone who passed
(SELECT StudId FROM GRADES
WHERE CourId = 'M214'
AND GRADE IS NOT NULL);
Can be done with join:
SELECT FName
FROM STUDENT s, GRADES g
WHERE s.StudId = g.StudId AND g.CourId = 'M214'
AND g.Grade IS NOT NULL;
Correlated Nested Queries
- Consume a lot more computation
- If the WHERE condition of the nested query refers to attributes of a relation declared in the outer query, they are correlated
Retrieve names of employees that worked more hours on a project than the average number of hours on that same project
SELECT e.FName
FROM EMPLOYEES e, WORKS_ON w
WHERE e.EmployId = w.EmployId AND
w.NoOfHours > (SELECT AVG(NoOfHours) -- gets avg for a project
FROM WORK_ON w1
WHERE w.ProjId = w1.ProjId); -- on same project
)
SELECT e.FName
FROM EMPLOYEES e
WHERE 3 > ( -- only select the employee that has < 3 employees with a higher sal
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM EMPLOYEES e1
WHERE e1.salary > e.salary -- e.salary is a correlated attribute
);
SELECT e.FName
-- avergage employee sal
-- total num of hours
-- total > 1000
Exercises
In SQL, specify the following queries on the COMPANY database using the concept of nested queries.
EMPLOYEE
- Fname
- Minit
- Lname
- Ssn
- Bdate
- Address
- Sex
- Salary
- Super_Ssn
- Dno
DEPARTMENT
- Dname
- Dnumber
- Mgr_ssn
- Mgr_start_date
DEPT_LOCATIONS
- Dnumber
- Dlocation
PROJECT
- Pname
- Pnumber
- Plocation
- Dnum
WORKS_ON
- Essn
- Pno
- Hours
DEPENDENT
- Essn
- Dependent_name
- Sex
- Bdate
- Relationship
- Retrieve the names of all employees who work in the department that has the employee with the highest salary among all employees.
SELECT e.Fname
FROM EMPLOYEE e
WHERE e.DepNo = ( -- matching Depno with highest sal
-- find highest salry
SELECT DepNo
FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE Salary = (
SELECT MAX(Salary)
FROM EMPLOYEE
)
);
- Retrieve the names of all employees whose supervisor's supervisor has '888665555' for Ssn.
-- all supervisors
SELECT e.FName
FROM EMPLOYEE e
WHERE (
SELECT e1.SuperSSN -- supervisors supervisor
FROM EMPLOYEE e1
WHERE e1.SSN = (SELECT e2.SuperSSN
FROM EMPLOYEE e2)
) = '888665555'
AND e2.SSN = e.SSN;
- Retrieve the names of employees who make at least $10,000 more than the employee who is paid the least in the company
SELECT e.FName
FROM EMPLOYEE e
-- Find person paid least
WHERE e.salary >= ((
-- find lowest salry
SELECT e1.salary
FROM EMPLOYEE e1
ORDER BY salary ASC
LIMIT 1
)+10000);
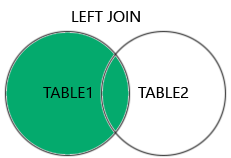
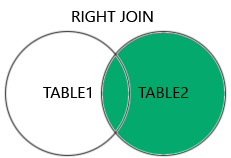
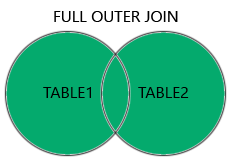
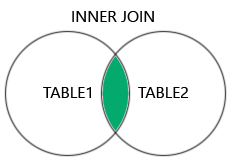
JOIN
- INNER (
theta join,equi-join,natural join) - OUTER (
left,right,full) equi-joinis most common- Based on a (FK,PK) pair
SELECT *
FROM r1,r2
WHERE r1.B = r2.B; -- this is a equi-join
If no join condition put, will return the Cartesian Product of the two relations.
SELECT * FROM r1,r2; -- will return r1 X r2
Grouping
- Create groups of tuples used to apply an aggregate function to
-- for each student, retrive number of courses passed
SELECT StudId, COUNT(*)
FROM GRADES
WHERE Grade IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY StudId;
| StudId | COUNT(*) |
|---|---|
| 300111 | 3 |
| 300121 | 2 |
HAVING
- Filters groups of tuples
- (While
WHEREfilters individual tuples)
SELECT StudId, COUNT(*)
FROM STUDENT s
NATURAL JOIN GRADES g
WHERE Grade IS NOT NULL and s.Major = 'Comp'
GROUP BY StudId
HAVING COUNT(*) > 2; -- as conditions are grouped, instead of indivdual tuples